マーケティング - スマートフォンセンサーを用いた人の位置推定および行動推定
Marketing
- Human Positioning and Activity Estimation using Smartphone Sensors
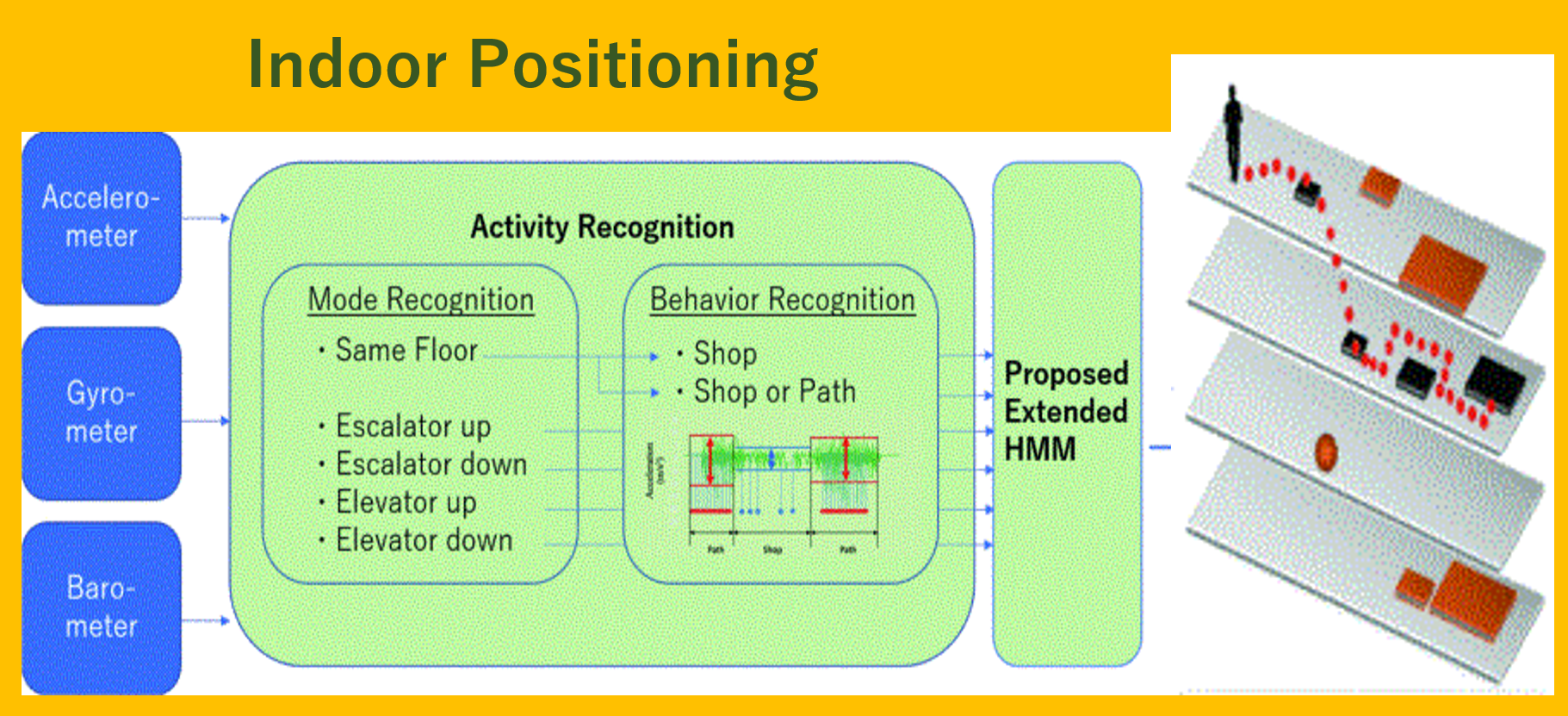
GPSによる位置推定の精度が下がるショッピングモールなどの大規模屋内施設に焦点を当て、コンテキストベースのマッチマッピングをによる正確な屋内測位システムを提案します。 本提案では、現在広く普及しているスマートフォンのモーションセンサを測位システムに用いています。 測位システムはまず、モーションセンサの情報から歩行者推測航法-Pedestrian Dead Reckoning (PDR)による使用者の軌道と人間活動を推定します. 本研究では、人間活動を2つのタイプに分け分析しています。 一つは、エスカレーターやエレベーターによるフロア間の移動。もう一つは、店内での買い物、通路での移動など同じフロアでの移動です。 その後、推定された人間活動をもとに位置推定を行います。 具体的には、LSTMによる人間活動の推定結果と、PDR軌道、および2.5次元屋内マップが隠れマルコフモデル (HMM) に統合され正確な屋内位置推定を行います。 2.5次元マップにはエスカレーターや各店舗などの屋内施設の位置情報が含まれています。 このシステムは、平均で2.21メートルの位置決め誤差を持ち、「ショップレベル」のパフォーマンスを達成しています。
With the advancement of electronic techniques, current smartphones can record location information with the help of WIFI signal, base station signal and Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers embedded in them. A smartphone can record where we go and where we stay. However, all the locations are recorded using latitude and longitude, which makes it hard for users to have an intuitive feelings of these data. In this paper, we propose a way to find places where users stay for a while to perform some activities with the location data tracked by smartphone, and use a cascade classifier to infer users' different activities in different places. With places and related activities, we can build a lifelog for smartphone users.